By Mithun Srivastava- Automate to Profit | Published January 2025
The affiliate marketing landscape has undergone a dramatic transformation in recent years, driven by privacy regulations, browser changes, and evolving consumer expectations. Traditional tracking methods that once provided reliable attribution data are now facing significant challenges, forcing affiliate marketers to adapt their strategies and embrace new technologies. In 2025, successful affiliate tracking requires a sophisticated understanding of multiple attribution methods, privacy-compliant data collection, and advanced analytics techniques.
The stakes for accurate tracking have never been higher. With iOS 14.5+ privacy changes, third-party cookie deprecation, and stricter privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, affiliate marketers who rely on outdated tracking methods are losing substantial revenue to attribution gaps. Industry research indicates that marketers using advanced server-side tracking recover 30-40% more conversions compared to those relying solely on traditional pixel-based methods [1].
This comprehensive guide explores the current state of affiliate tracking and attribution, providing actionable strategies for implementing robust tracking systems that deliver accurate data while respecting user privacy. We’ll examine the strengths and limitations of different tracking approaches, provide step-by-step implementation guidance, and share optimization strategies that maximize attribution accuracy in today’s challenging environment.
Table of Contents
1.The Evolution of Affiliate Tracking
2.Understanding Modern Attribution Challenges
3.Pixel Tracking: Traditional Methods and Current Limitations
4.Postback Tracking: Server-to-Server Communication
5.Server-Side Tracking: The Future of Attribution
6.GA4 Integration and UTM Best Practices
7.Hybrid Tracking Strategies
8.Privacy Compliance and Data Protection
9.Implementation Guide and Technical Setup
10.Performance Optimization and Troubleshooting
11.Future-Proofing Your Tracking Strategy
The Evolution of Affiliate Tracking {#evolution-of-tracking}
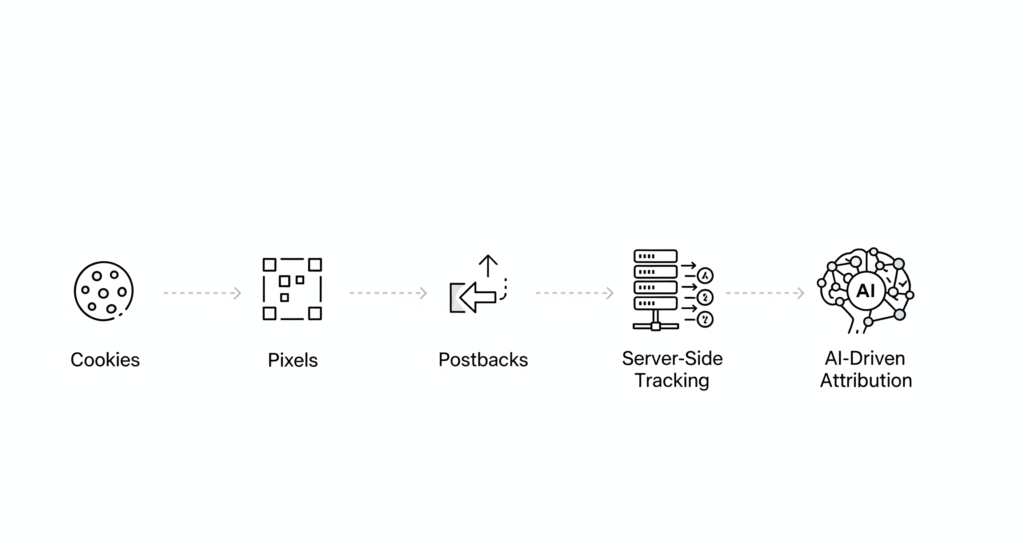
Affiliate tracking has undergone multiple evolutionary phases since the inception of performance marketing in the mid-1990s. Each phase has been driven by technological advances, changing user behaviors, and regulatory developments that have shaped how marketers collect, process, and utilize attribution data. Understanding this evolution provides crucial context for navigating today’s complex tracking landscape and preparing for future developments.
The Cookie-Based Era (1995-2020)
The early days of affiliate tracking were built on the foundation of HTTP cookies, small text files stored in users’ browsers that enabled cross-site tracking and attribution. This period was characterized by relatively simple tracking implementations and high attribution accuracy, as cookies provided persistent identifiers that could reliably connect user actions across multiple sessions and websites.
First-party cookies, set by the domain the user was visiting, provided reliable session tracking and basic user identification. These cookies enabled affiliate networks to track user journeys from initial click to final conversion, creating clear attribution paths that supported commission calculations and performance optimization. The simplicity and reliability of cookie-based tracking made it the dominant approach for nearly two decades.
Third-party cookies expanded tracking capabilities by enabling cross-domain attribution and audience building. These cookies, set by domains other than the one being visited, allowed affiliate networks and advertising platforms to track users across multiple websites, creating comprehensive profiles that supported advanced targeting and attribution modeling. The widespread adoption of third-party cookies enabled sophisticated affiliate marketing strategies that relied on detailed user behavior data.
Cookie pooling and syncing technologies emerged to address limitations in cross-domain tracking, enabling different platforms to share user identifiers and create unified tracking systems. These technologies allowed affiliate networks, advertisers, and publishers to coordinate their tracking efforts, reducing attribution gaps and improving campaign performance measurement.
The cookie-based era reached its peak in the 2010s, when sophisticated attribution models, audience segmentation, and personalization strategies all relied heavily on cookie data. However, this period also saw the emergence of privacy concerns and regulatory scrutiny that would eventually lead to the decline of cookie-based tracking.
The Privacy Revolution (2018-Present)
The introduction of GDPR in 2018 marked the beginning of a fundamental shift in how digital marketing approaches data collection and user privacy. This regulation, followed by similar laws worldwide, established new requirements for user consent, data transparency, and privacy protection that directly impacted affiliate tracking strategies.
Browser-initiated privacy changes accelerated the decline of traditional tracking methods. Safari’s Intelligent Tracking Prevention (ITP), introduced in 2017 and continuously updated, began blocking third-party cookies and limiting first-party cookie lifespans. Firefox followed with Enhanced Tracking Protection, and Chrome announced plans to phase out third-party cookies entirely, though this timeline has been repeatedly delayed.
The iOS 14.5 update in 2021 introduced App Tracking Transparency (ATT), requiring apps to request explicit permission before tracking users across other apps and websites. This change dramatically reduced the availability of user-level data for mobile attribution, forcing affiliate marketers to adapt their strategies for a post-IDFA world.
Privacy-focused browsers and browser extensions gained popularity among users seeking greater control over their data. These tools actively block tracking scripts, delete cookies, and prevent cross-site data collection, creating additional challenges for affiliate marketers who rely on traditional tracking methods.
The cumulative impact of these privacy changes has been substantial. Many affiliate marketers report attribution gaps of 20-40% compared to pre-privacy regulation performance, with mobile campaigns particularly affected. These gaps represent not just measurement challenges, but actual revenue losses due to inability to optimize campaigns effectively.
The Server-Side Transition (2020-Present)
The limitations of client-side tracking have driven widespread adoption of server-side tracking solutions that process data on the server rather than in the user’s browser. This approach offers several advantages, including improved data accuracy, reduced impact from ad blockers, and better privacy compliance capabilities.
Server-side tracking architectures move data collection and processing from the client (browser) to the server, where it can be handled more reliably and securely. This approach reduces dependence on cookies and browser-based tracking technologies, providing more consistent data collection across different devices and browsers.
First-party data strategies have become increasingly important as third-party data sources become less reliable. Affiliate marketers are investing in building direct relationships with their audiences, collecting data through owned channels, and creating unified customer profiles that don’t rely on cross-site tracking.
API-based attribution systems enable direct communication between different platforms without relying on browser-based tracking. These systems use server-to-server communication to share attribution data, reducing dependence on client-side technologies that may be blocked or restricted.
Privacy-compliant tracking solutions have emerged that provide attribution capabilities while respecting user privacy preferences. These solutions often use techniques such as data aggregation, differential privacy, and consent management to balance marketing needs with privacy requirements.
Current State and Challenges
Today’s affiliate tracking landscape is characterized by fragmentation, complexity, and ongoing uncertainty about future developments. Marketers must navigate a complex ecosystem of different tracking methods, each with its own strengths, limitations, and implementation requirements.
Attribution accuracy has become a significant challenge, with many marketers reporting substantial gaps between actual performance and measured results. These gaps make it difficult to optimize campaigns effectively and can lead to misallocation of marketing resources. The challenge is particularly acute for campaigns that rely on longer attribution windows or complex customer journeys.
Cross-device tracking has become increasingly difficult as traditional methods lose effectiveness. Users frequently switch between devices during their purchase journeys, making it challenging to create unified attribution paths. This challenge is particularly problematic for high-consideration purchases that involve extended research and comparison phases.
Data quality issues have emerged as tracking becomes more complex and fragmented. Different tracking methods may report conflicting data, making it difficult to establish single sources of truth for campaign performance. These discrepancies can lead to confusion and poor decision-making if not properly managed.
Technical complexity has increased dramatically as marketers implement multiple tracking solutions to address different challenges. Managing these complex systems requires specialized knowledge and ongoing maintenance that can strain marketing teams and budgets.
Emerging Solutions and Technologies
The industry has responded to tracking challenges by developing new technologies and approaches that promise to restore attribution accuracy while respecting privacy requirements. These emerging solutions represent the next phase in the evolution of affiliate tracking.
Enhanced conversion tracking uses first-party data to improve attribution accuracy without relying on third-party cookies. These solutions typically involve collecting user information through owned channels and using it to enhance conversion tracking and attribution modeling.
Machine learning attribution models use artificial intelligence to identify patterns in available data and make predictions about attribution paths that may not be directly observable. These models can help fill attribution gaps by inferring connections between marketing touchpoints and conversions.
Blockchain-based tracking solutions promise to provide transparent, tamper-proof attribution data that can be verified by all parties involved in affiliate campaigns. While still in early stages, these solutions could address trust and transparency issues that have long plagued affiliate marketing.
Privacy-preserving technologies such as differential privacy and federated learning enable data analysis and attribution modeling while protecting individual user privacy. These technologies allow for aggregate insights without exposing individual user data.
Unified measurement platforms attempt to consolidate data from multiple sources and tracking methods to provide comprehensive attribution insights. These platforms use advanced data processing and modeling techniques to reconcile discrepancies between different tracking approaches and provide unified performance views.
Understanding Modern Attribution Challenges {#attribution-challenges}
The modern affiliate marketing ecosystem faces unprecedented challenges in accurately attributing conversions to their originating sources. These challenges stem from a complex interplay of technological changes, regulatory requirements, and evolving user behaviors that have fundamentally altered how data flows through digital marketing systems. Understanding these challenges is essential for developing effective tracking strategies that deliver reliable attribution data in today’s environment.
The Attribution Gap Phenomenon
Attribution gaps represent the difference between actual marketing performance and what can be measured through available tracking methods. These gaps have grown significantly in recent years, with many affiliate marketers reporting 20-40% of conversions that cannot be accurately attributed to their originating sources. This phenomenon has profound implications for campaign optimization, budget allocation, and performance measurement.
The primary driver of attribution gaps is the breakdown of traditional tracking mechanisms that relied on persistent identifiers and cross-site data sharing. As browsers implement stricter privacy controls and users adopt privacy-focused tools, the ability to track user journeys across multiple touchpoints has been severely compromised. This breakdown is particularly pronounced for campaigns that involve longer consideration periods or complex customer journeys.
Mobile attribution gaps tend to be even more severe than desktop gaps, particularly following the implementation of iOS 14.5+ privacy changes. The App Tracking Transparency framework requires explicit user consent for cross-app tracking, and opt-in rates typically range from 15-25% across most industries. This means that 75-85% of iOS users cannot be tracked using traditional methods, creating substantial blind spots in mobile campaign measurement.
Cross-device attribution has become increasingly challenging as users frequently switch between devices during their purchase journeys. Traditional tracking methods struggle to connect user actions across different devices, leading to fragmented attribution paths that underestimate the true impact of marketing touchpoints. This challenge is particularly problematic for high-consideration purchases where research and comparison phases may span multiple devices and sessions.
The compounding effect of multiple attribution challenges means that the total impact on measurement accuracy is often greater than the sum of individual issues. When browser restrictions, privacy regulations, ad blockers, and cross-device challenges all affect the same campaign, the resulting attribution gaps can be substantial enough to make campaign optimization extremely difficult.
Browser and Platform Restrictions
Modern browsers have implemented increasingly sophisticated tracking prevention mechanisms that directly impact affiliate marketing attribution. These restrictions are designed to protect user privacy but create significant challenges for marketers who rely on accurate attribution data for campaign optimization and performance measurement.
Safari’s Intelligent Tracking Prevention (ITP) has evolved through multiple versions, each introducing new restrictions on tracking capabilities. Current versions of ITP limit first-party cookie lifespans, block third-party cookies entirely, and implement sophisticated algorithms to identify and prevent cross-site tracking attempts. These restrictions affect not just display advertising but also affiliate link tracking and conversion attribution.
Firefox’s Enhanced Tracking Protection operates similarly to Safari’s ITP but with some differences in implementation and scope. The browser blocks known tracking domains, restricts cookie access, and implements fingerprinting protection that can interfere with some tracking methods. Firefox’s approach tends to be more aggressive in some areas while providing more flexibility in others.
Chrome’s privacy initiatives, while less restrictive than Safari and Firefox, still impact affiliate tracking capabilities. The browser has implemented SameSite cookie restrictions, plans to phase out third-party cookies, and has introduced various privacy-focused features that affect data collection. Chrome’s large market share means that even minor changes can have significant impacts on affiliate marketing campaigns.
Mobile platform restrictions add another layer of complexity to attribution challenges. iOS restrictions on cross-app tracking, Android’s privacy improvements, and app store policies all affect how affiliate marketers can track and attribute mobile conversions. These restrictions are particularly challenging for affiliate campaigns that involve mobile app installations or in-app purchases.
The inconsistency between different browsers and platforms creates additional complexity for affiliate marketers who must account for varying tracking capabilities across different user segments. A tracking method that works well for Chrome users on desktop may be completely ineffective for Safari users on mobile, requiring sophisticated attribution strategies that adapt to different environments.
Privacy Regulation Impact
Privacy regulations have fundamentally changed how affiliate marketers can collect, process, and utilize user data for attribution purposes. These regulations establish legal requirements that often conflict with traditional tracking methods, forcing marketers to balance attribution accuracy with compliance obligations.
GDPR requirements for explicit consent have significantly impacted data collection capabilities across European markets. The regulation requires clear, specific consent for data processing activities, including tracking and attribution. Many users decline consent when presented with tracking requests, creating attribution gaps for European traffic that can be substantial.
CCPA and similar state-level privacy laws in the United States have introduced additional compliance requirements that affect affiliate tracking strategies. These laws provide users with rights to know what data is collected, request deletion of personal information, and opt out of data sales. Compliance with these requirements often involves implementing tracking restrictions that impact attribution accuracy.
Sector-specific regulations add additional layers of complexity for affiliate marketers operating in regulated industries. Financial services, healthcare, and other regulated sectors often have additional data protection requirements that further restrict tracking capabilities. These restrictions can make it particularly challenging to implement comprehensive attribution strategies in these verticals.
International data transfer restrictions affect affiliate marketers who operate across multiple jurisdictions. Regulations such as GDPR place restrictions on transferring personal data outside of specific regions, which can complicate the implementation of global tracking and attribution systems. These restrictions often require sophisticated data processing architectures that maintain compliance while enabling effective attribution.
The ongoing evolution of privacy regulations means that compliance requirements continue to change, creating uncertainty about future tracking capabilities. Marketers must stay current with regulatory developments and be prepared to adapt their tracking strategies as new requirements are implemented.
Technical Infrastructure Challenges
Modern affiliate tracking requires sophisticated technical infrastructure that can handle complex data flows, multiple attribution methods, and privacy compliance requirements. Many affiliate marketers struggle with the technical complexity of implementing and maintaining these systems effectively.
Data integration challenges arise when attempting to combine data from multiple tracking sources into unified attribution models. Different tracking methods may use different data formats, attribution windows, and measurement approaches, making it difficult to create consistent performance views. These integration challenges often require specialized technical expertise and sophisticated data processing capabilities.
Real-time processing requirements have increased as marketers seek to optimize campaigns based on immediate performance feedback. However, implementing real-time attribution systems requires robust technical infrastructure that can handle high data volumes and complex processing requirements. Many affiliate marketers lack the technical resources to implement these systems effectively.
Scalability concerns emerge as tracking systems must handle growing data volumes and increasing complexity. As affiliate programs grow and tracking requirements become more sophisticated, the underlying technical infrastructure must be able to scale accordingly. This scaling often requires significant technical investment and ongoing maintenance.
Data quality management becomes increasingly important as tracking systems become more complex and data sources multiply. Ensuring data accuracy, consistency, and completeness across multiple tracking methods requires sophisticated quality assurance processes and ongoing monitoring. Poor data quality can undermine attribution accuracy and lead to poor campaign optimization decisions.
Security requirements for attribution systems have increased as privacy regulations and data protection concerns have grown. Tracking systems must implement appropriate security measures to protect user data while maintaining the functionality necessary for effective attribution. These security requirements often add complexity and cost to tracking implementations.
User Behavior Evolution
User behaviors have evolved in ways that make traditional attribution approaches less effective. These behavioral changes reflect growing privacy awareness, changing device usage patterns, and evolving expectations about data collection and usage.
Privacy-conscious behaviors have become more common as users become more aware of data collection practices and their implications. Many users actively delete cookies, use private browsing modes, employ ad blockers, or use privacy-focused browsers. These behaviors directly impact the effectiveness of traditional tracking methods and create attribution gaps.
Multi-device usage patterns have become more complex as users seamlessly switch between smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other connected devices during their purchase journeys. Traditional tracking methods struggle to connect user actions across these different devices, leading to fragmented attribution paths that underestimate marketing impact.
Ad blocker adoption continues to grow, particularly among certain demographic groups and in specific geographic regions. Ad blockers don’t just block advertisements; they also block many tracking scripts and pixels used for attribution purposes. This blocking creates blind spots in attribution data that can significantly impact campaign measurement accuracy.
Incognito and private browsing usage has increased as users become more privacy-conscious. These browsing modes typically don’t store cookies or other tracking data, making it impossible to attribute conversions that occur during private browsing sessions. The impact of private browsing on attribution accuracy varies by audience but can be substantial for privacy-conscious user segments.
Cross-platform shopping behaviors have become more sophisticated as users research products across multiple channels before making purchases. Users might discover products through social media, research them on comparison sites, read reviews on different platforms, and ultimately make purchases through entirely different channels. These complex journeys are difficult to track using traditional attribution methods.
Measurement Methodology Limitations
Traditional attribution models and measurement methodologies have limitations that become more pronounced in today’s complex digital environment. These limitations affect how accurately affiliate marketers can assess campaign performance and make optimization decisions.
Last-click attribution models, while simple to implement and understand, significantly undervalue the contribution of upper-funnel marketing activities. In affiliate marketing, this can lead to over-investment in bottom-funnel activities while under-investing in awareness and consideration-stage marketing that drives long-term growth.
First-click attribution models have the opposite problem, overvaluing initial touchpoints while undervaluing the activities that actually drive conversions. This model can lead to over-investment in awareness activities while neglecting the optimization of conversion-focused campaigns.
Linear attribution models attempt to address the limitations of single-touch models by distributing credit equally across all touchpoints. However, this approach assumes that all touchpoints contribute equally to conversions, which is rarely accurate in practice. The equal weighting can lead to suboptimal budget allocation and campaign optimization decisions.
Time-decay attribution models give more credit to touchpoints closer to conversion, which can be more accurate than linear models but still may not reflect the true contribution of different marketing activities. The arbitrary nature of time-decay curves means that these models may not accurately represent the actual influence of different touchpoints.
Data-driven attribution models promise to provide more accurate attribution by using machine learning to analyze actual conversion patterns. However, these models require large amounts of data to function effectively and may not work well for smaller affiliate programs or niche markets. Additionally, the “black box” nature of these models can make it difficult to understand and act on their insights.
Industry-Specific Challenges
Different industries face unique attribution challenges based on their customer behaviors, regulatory environments, and business models. Understanding these industry-specific challenges is important for developing effective tracking strategies that address sector-specific requirements.
E-commerce attribution faces challenges related to long consideration periods, comparison shopping behaviors, and seasonal purchasing patterns. Customers often research products across multiple sessions and devices before making purchases, creating complex attribution paths that are difficult to track accurately. Additionally, return and refund behaviors can complicate attribution calculations and commission structures.
Financial services attribution must navigate strict regulatory requirements while dealing with high-consideration purchase decisions that often involve offline interactions. The sensitive nature of financial data creates additional privacy and security requirements that can limit tracking capabilities. Additionally, the long sales cycles common in financial services make attribution window decisions particularly important.
Healthcare and pharmaceutical affiliate marketing faces unique regulatory restrictions that limit data collection and tracking capabilities. HIPAA and similar regulations create strict requirements for handling health-related data, which can significantly impact attribution strategies. Additionally, the sensitive nature of health-related purchases means that users may be particularly privacy-conscious in these contexts.
B2B affiliate marketing deals with complex, multi-stakeholder decision-making processes that can span months or years. Traditional attribution models struggle to account for the multiple touchpoints and influencers involved in B2B purchase decisions. Additionally, the high value of B2B transactions means that attribution accuracy is particularly important for campaign optimization and commission calculations.
Travel and hospitality attribution faces challenges related to seasonal booking patterns, long planning horizons, and complex itineraries that may involve multiple bookings. The industry’s reliance on comparison shopping and the influence of reviews and recommendations create complex attribution paths that are difficult to track accurately.
Pixel Tracking: Traditional Methods and Current Limitations {#pixel-tracking}

Pixel tracking has served as the backbone of affiliate marketing attribution for over two decades, providing a simple yet effective method for connecting user actions to marketing touchpoints. However, the changing digital landscape has exposed significant limitations in pixel-based tracking that affiliate marketers must understand and address. While pixel tracking remains relevant in certain contexts, its effectiveness has been substantially reduced by privacy changes, browser restrictions, and evolving user behaviors.
Understanding Pixel Tracking Technology
Pixel tracking operates through small, invisible images (typically 1×1 pixels) embedded in web pages, emails, or advertisements. When a user’s browser loads a page containing a tracking pixel, it automatically requests the pixel image from the tracking server, creating an opportunity to collect information about the user’s visit and behavior. This simple mechanism has enabled sophisticated tracking and attribution capabilities that have powered affiliate marketing growth for decades.
The technical implementation of pixel tracking involves placing HTML image tags or JavaScript code snippets on relevant web pages, typically conversion pages where affiliate commissions should be recorded. When users complete desired actions, such as making purchases or submitting forms, their browsers automatically trigger pixel requests that notify affiliate networks or tracking platforms about the conversions.
Cookie integration has been a crucial component of pixel tracking effectiveness, enabling the connection of conversion events to earlier marketing touchpoints. When users click affiliate links, tracking cookies are typically set in their browsers. Later, when conversion pixels fire, these cookies are read to determine which affiliate should receive credit for the conversion. This cookie-pixel integration has enabled sophisticated attribution modeling and commission tracking.
JavaScript-enhanced pixels provide additional functionality beyond simple image-based tracking, enabling the collection of detailed page information, user behavior data, and dynamic parameter passing. These enhanced pixels can capture information such as purchase amounts, product details, user characteristics, and page engagement metrics that support more sophisticated attribution and optimization strategies.
Server-side pixel implementations attempt to address some limitations of client-side tracking by processing pixel requests on the server rather than relying entirely on browser-based functionality. However, these implementations still typically require some client-side components and remain subject to many of the same limitations as traditional pixel tracking.
Current Effectiveness and Limitations
The effectiveness of pixel tracking has declined significantly in recent years due to various technological and regulatory changes. While pixels continue to function in many contexts, their reliability and coverage have been substantially reduced, creating attribution gaps that impact campaign measurement and optimization.
Browser blocking has become a major limitation for pixel tracking effectiveness. Modern browsers implement increasingly sophisticated tracking prevention mechanisms that can block pixel requests, delete associated cookies, or prevent cross-site data sharing. Safari’s Intelligent Tracking Prevention, Firefox’s Enhanced Tracking Protection, and similar features in other browsers all impact pixel tracking reliability.
Ad blocker interference affects a significant percentage of users who have installed browser extensions or use browsers with built-in ad blocking capabilities. These tools often block tracking pixels along with advertisements, creating blind spots in attribution data. Ad blocker usage varies by demographic and geographic region but can affect 20-40% of users in some segments.
Cookie restrictions have undermined the attribution capabilities that depend on connecting pixel events to earlier touchpoints. Browser limitations on cookie lifespans, cross-site cookie access, and third-party cookie functionality all impact the ability to create accurate attribution paths using pixel-based methods.
Mobile limitations are particularly pronounced for pixel tracking, as mobile browsers often implement stricter privacy controls and users may have limited data connectivity that affects pixel loading. Additionally, mobile app environments present unique challenges for pixel implementation that don’t exist in web-based contexts.
Privacy regulation compliance creates additional constraints on pixel tracking implementation and effectiveness. GDPR, CCPA, and similar regulations often require explicit consent for tracking activities, and many users decline consent when presented with tracking requests. This consent requirement can significantly reduce the coverage of pixel-based tracking systems.
Implementation Best Practices
Despite their limitations, pixels remain an important component of comprehensive tracking strategies when implemented correctly. Following best practices can maximize pixel effectiveness while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations and technical requirements.
Proper pixel placement is crucial for accurate conversion tracking and attribution. Conversion pixels should be placed on pages that represent completed actions, such as order confirmation pages, thank you pages, or account creation success pages. The pixel should fire only when the desired action has been completed to ensure accurate conversion counting.
Dynamic parameter passing enables pixels to capture detailed information about conversions, including purchase amounts, product details, customer information, and other relevant data. This information supports more sophisticated commission calculations and campaign optimization strategies. Parameters should be properly encoded and validated to prevent data corruption or security issues.
Fallback mechanisms should be implemented to address situations where primary pixel tracking fails due to browser restrictions, connectivity issues, or other technical problems. These mechanisms might include server-side tracking components, alternative pixel implementations, or manual reporting processes that ensure important conversions are not lost.
Testing and validation procedures are essential for ensuring that pixel implementations work correctly across different browsers, devices, and user scenarios. Regular testing should verify that pixels fire correctly, parameters are passed accurately, and attribution data is recorded properly. Testing should include scenarios with ad blockers, privacy settings, and other conditions that might affect pixel functionality.
Privacy compliance measures must be integrated into pixel implementations to ensure adherence to applicable regulations. This includes implementing consent management systems, providing clear privacy disclosures, and ensuring that pixel data collection aligns with stated privacy policies and user expectations.
Advanced Pixel Strategies
Sophisticated affiliate marketers have developed advanced pixel strategies that attempt to maximize tracking effectiveness while working within the constraints of modern privacy and technical limitations. These strategies often involve multiple pixel implementations, enhanced data collection methods, and integration with other tracking approaches.
Multi-pixel implementations use different pixel technologies and placement strategies to maximize conversion capture rates. This approach might involve implementing both JavaScript and image-based pixels, using multiple tracking providers, or placing pixels in different locations to increase the likelihood of successful tracking.
Enhanced data collection through pixels can provide additional information that supports attribution modeling and campaign optimization. This might include collecting user agent information, referrer data, page engagement metrics, or other behavioral signals that help fill attribution gaps when traditional cookie-based attribution fails.
Cross-domain pixel strategies attempt to maintain tracking capabilities across different domains and subdomains. These strategies might involve pixel synchronization, domain-specific implementations, or centralized tracking systems that consolidate data from multiple sources.
Real-time pixel optimization uses dynamic pixel implementations that adapt based on user characteristics, browser capabilities, or other contextual factors. These systems might serve different pixel versions to different user segments or adjust pixel behavior based on detected privacy settings or restrictions.
Pixel data enrichment combines pixel-collected data with information from other sources to create more comprehensive attribution pictures. This enrichment might involve matching pixel data with CRM information, email engagement data, or other first-party data sources to improve attribution accuracy.
Integration with Modern Tracking Approaches
While pixel tracking alone is insufficient for comprehensive attribution in today’s environment, pixels can play important roles in integrated tracking strategies that combine multiple attribution methods. Understanding how to effectively integrate pixels with other tracking approaches is crucial for maximizing overall attribution accuracy.
Pixel-postback integration combines the immediate feedback of pixel tracking with the reliability of server-side postback systems. In this approach, pixels provide real-time conversion notifications while postbacks ensure that conversions are accurately recorded even if pixel tracking fails. This redundancy improves overall tracking reliability.
First-party data enhancement uses pixel-collected information to enrich first-party customer databases and improve attribution modeling. Pixels can capture behavioral data that is then matched with known customer information to create more complete attribution pictures that don’t rely entirely on cross-site tracking.
Machine learning integration uses pixel data as input for attribution models that attempt to fill gaps in tracking coverage. These models can use available pixel data along with other signals to make predictions about attribution paths that may not be directly observable through traditional tracking methods.
Cross-channel attribution integration combines pixel data with information from other marketing channels to create unified attribution models. This integration helps ensure that pixel-tracked conversions are properly attributed within broader marketing attribution frameworks that account for multiple touchpoints and channels.
Privacy-compliant pixel strategies focus on maximizing tracking effectiveness while respecting user privacy preferences and regulatory requirements. These strategies might involve consent-based pixel implementations, data minimization approaches, or privacy-preserving data collection methods that maintain attribution capabilities while protecting user privacy.
Future of Pixel Tracking
The future of pixel tracking in affiliate marketing will likely involve continued evolution to address privacy concerns and technical limitations while maintaining attribution capabilities. Understanding likely future developments can help affiliate marketers prepare their tracking strategies for continued effectiveness.
Privacy-preserving pixel technologies are being developed that provide attribution capabilities while protecting individual user privacy. These technologies might use techniques such as differential privacy, data aggregation, or cryptographic methods to enable attribution without exposing individual user data.
Browser-native attribution APIs are being developed by major browser vendors to provide standardized attribution capabilities that work within privacy constraints. These APIs might eventually replace traditional pixel tracking with browser-controlled attribution systems that balance marketing needs with privacy protection.
Server-side pixel processing is likely to become more common as marketers seek to reduce dependence on client-side tracking technologies. These approaches move pixel processing to the server side while maintaining compatibility with existing pixel-based systems and workflows.
Consent-based pixel optimization will likely become more sophisticated as privacy regulations evolve and user expectations change. These optimizations might involve dynamic consent management, granular privacy controls, or user-controlled attribution preferences that allow individuals to balance privacy with personalized experiences.
Integration with emerging technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and privacy-preserving computation may create new possibilities for pixel-based attribution that address current limitations while maintaining or improving attribution accuracy.
Postback Tracking: Server-to-Server Communication {#postback-tracking}
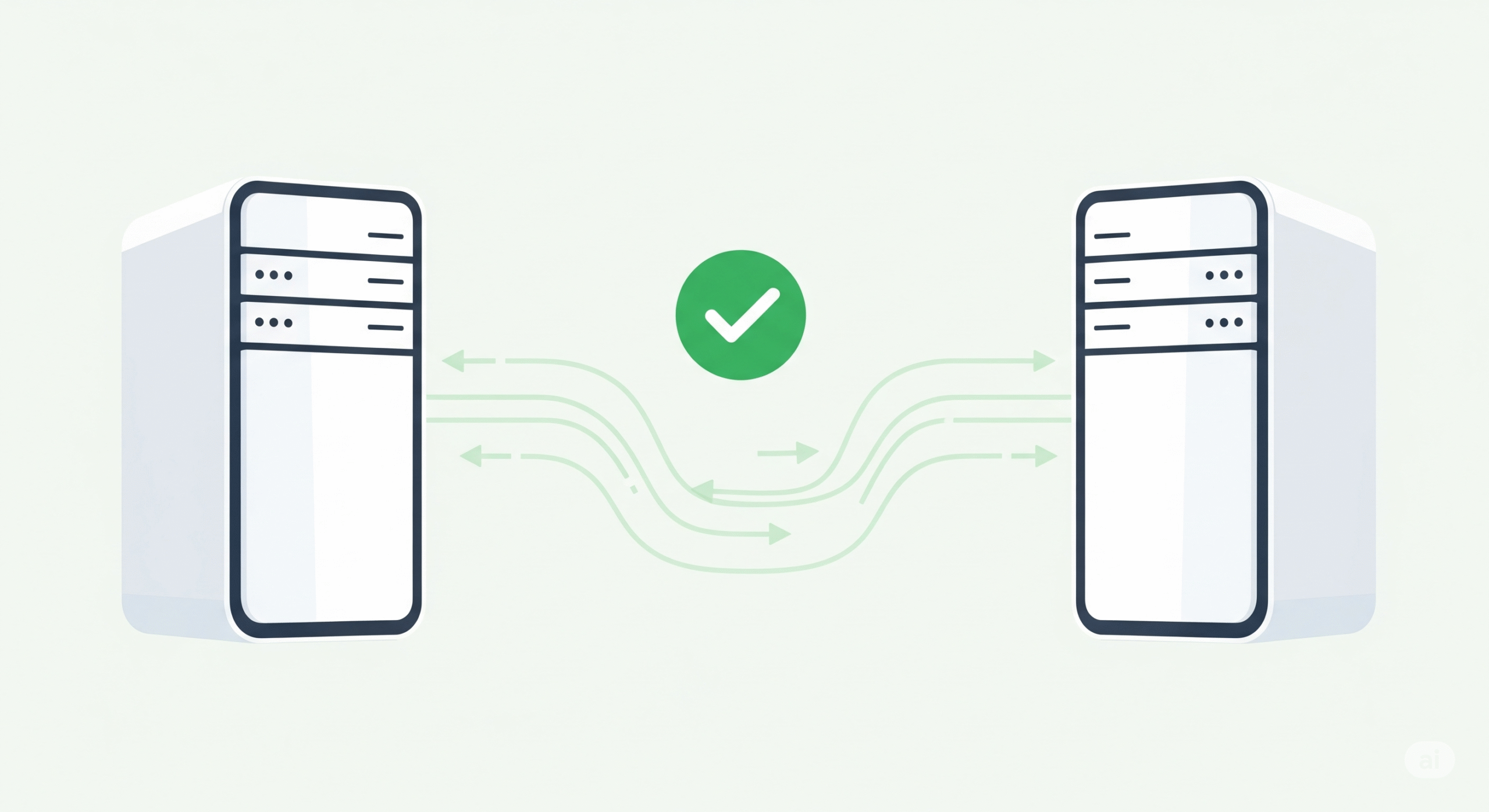
Postback tracking represents a fundamental shift from client-side attribution methods to server-side communication systems that provide more reliable and privacy-compliant tracking capabilities. Unlike pixel tracking, which relies on browser-based technologies that can be blocked or restricted, postback tracking uses direct server-to-server communication to transmit conversion data. This approach has become increasingly important as traditional tracking methods face growing limitations from privacy regulations and browser restrictions.
Understanding Postback Architecture
Postback tracking operates through HTTP requests sent directly between servers, bypassing the user’s browser entirely. When a conversion occurs, the advertiser’s server sends a postback URL request to the affiliate network or tracking platform, including relevant conversion data as URL parameters. This server-to-server communication ensures that conversion data is transmitted reliably, regardless of browser settings, privacy controls, or client-side restrictions.
The technical architecture of postback tracking involves several key components working together to ensure accurate attribution and data transmission. The advertiser’s conversion tracking system must be configured to detect completed actions and trigger appropriate postback requests. These systems typically monitor database changes, order completions, or other server-side events that indicate successful conversions.
Postback URL construction involves encoding conversion data into HTTP requests that can be processed by receiving systems. These URLs typically include parameters such as conversion IDs, affiliate IDs, commission amounts, product information, and other relevant data needed for attribution and commission calculations. Proper URL encoding and parameter validation are crucial for ensuring data integrity and system compatibility.
Authentication and security mechanisms protect postback communications from fraud and ensure that conversion data comes from legitimate sources. These mechanisms might include API keys, digital signatures, IP address restrictions, or other security measures that verify the authenticity of postback requests. Strong security is essential for maintaining trust in affiliate marketing relationships.
Error handling and retry logic ensure that postback communications are delivered successfully even when temporary network issues or server problems occur. Robust postback systems include mechanisms for detecting failed transmissions, implementing retry strategies, and providing fallback communication methods when primary systems are unavailable.
Advantages Over Client-Side Tracking
Postback tracking offers several significant advantages over traditional client-side tracking methods, making it an essential component of modern affiliate marketing attribution strategies. These advantages address many of the limitations that have reduced the effectiveness of pixel-based tracking in recent years.
Reliability represents the most significant advantage of postback tracking, as server-to-server communication is not affected by browser restrictions, ad blockers, or privacy settings that can interfere with client-side tracking. Postback requests are sent directly between servers, ensuring that conversion data is transmitted regardless of user browser configurations or privacy preferences.
Privacy compliance is enhanced through postback tracking because the communication occurs entirely on the server side, without requiring client-side data collection or cross-site tracking. This approach aligns better with privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, as it reduces the need for user consent and minimizes personal data exposure during the attribution process.
Data accuracy improves with postback tracking because conversion detection occurs on the server side, where it can be integrated directly with order processing systems, payment gateways, and other authoritative data sources. This integration reduces the risk of conversion counting errors and ensures that attribution data reflects actual business outcomes rather than just user actions.
Fraud prevention capabilities are enhanced through postback tracking because server-side validation can verify conversion authenticity before transmitting attribution data. This validation might include checking payment status, verifying customer information, or implementing other fraud detection measures that are not possible with client-side tracking alone.
Real-time processing enables immediate conversion notification and attribution through postback systems. Unlike pixel tracking, which may be delayed or blocked, postback requests can be sent immediately when conversions occur, enabling faster campaign optimization and more responsive affiliate program management.
Implementation Strategies
Successful postback tracking implementation requires careful planning and attention to technical details that ensure reliable data transmission and accurate attribution. The implementation process involves configuring both sending and receiving systems to handle postback communications effectively.
Conversion detection systems must be configured to identify completed actions and trigger appropriate postback requests. This configuration typically involves integrating tracking code with order processing systems, payment gateways, or other business systems that can definitively identify successful conversions. The detection logic should account for different conversion types and ensure that postbacks are sent only for valid, completed actions.
Parameter mapping defines how conversion data is encoded into postback URLs and ensures that receiving systems can properly interpret and process the transmitted information. This mapping should include all relevant data needed for attribution and commission calculations, such as order values, product information, customer details, and timing data. Consistent parameter naming and formatting are crucial for system compatibility.
Security implementation protects postback communications from fraud and ensures data integrity during transmission. This implementation might include API key authentication, request signing, IP address validation, or other security measures appropriate for the specific use case and risk profile. Security measures should balance protection with system performance and reliability.
Testing and validation procedures verify that postback implementations work correctly under various conditions and scenarios. This testing should include successful conversion scenarios, error conditions, retry logic, and security validations. Comprehensive testing helps identify and resolve issues before they impact live affiliate campaigns.
Monitoring and alerting systems track postback performance and notify administrators of delivery failures, security issues, or other problems that might affect attribution accuracy. These systems should provide detailed logging and reporting capabilities that enable troubleshooting and performance optimization.
Advanced Postback Techniques
Sophisticated affiliate marketers and networks have developed advanced postback techniques that maximize attribution accuracy while addressing complex tracking scenarios and business requirements. These techniques often involve multiple postback implementations, enhanced data processing, and integration with other tracking methods.
Multi-postback strategies use different postback endpoints and configurations to ensure maximum delivery reliability and data redundancy. This approach might involve sending postbacks to multiple affiliate networks, backup tracking systems, or internal analytics platforms. Multi-postback implementations provide insurance against system failures while enabling comprehensive data collection.
Conditional postback logic adapts postback behavior based on conversion characteristics, customer attributes, or other contextual factors. This logic might involve different postback configurations for different product categories, customer segments, or geographic regions. Conditional logic enables more sophisticated attribution strategies that account for business complexity.
Delayed postback processing handles scenarios where conversion confirmation requires time for verification, payment processing, or fraud detection. These systems might implement delayed postback schedules that send initial notifications immediately followed by confirmation postbacks after verification processes are complete. Delayed processing ensures attribution accuracy while maintaining real-time campaign feedback.
Enhanced data transmission includes additional information in postback requests that supports advanced attribution modeling and campaign optimization. This enhanced data might include customer lifetime value predictions, product margin information, seasonal factors, or other business intelligence that enables more sophisticated campaign management.
Postback aggregation and batching optimize system performance by combining multiple conversion events into single postback requests. This approach can reduce server load and network traffic while maintaining attribution accuracy. Aggregation strategies must balance efficiency with real-time reporting requirements and system reliability.
Integration with Attribution Models
Postback tracking data serves as a crucial input for sophisticated attribution models that attempt to provide comprehensive views of marketing performance across multiple channels and touchpoints. Understanding how to effectively integrate postback data with attribution modeling is essential for maximizing the value of server-side tracking investments.
Last-click attribution models can be enhanced through postback data that provides definitive conversion information and accurate timing data. Postback-powered last-click models offer improved accuracy compared to client-side implementations because they rely on server-side conversion detection rather than browser-based tracking that may be incomplete or inaccurate.
Multi-touch attribution models benefit from postback data that provides reliable conversion endpoints for attribution calculations. While postbacks typically don’t provide complete customer journey information, they can serve as authoritative conversion records that anchor more complex attribution models that incorporate data from multiple sources.
Data-driven attribution models can use postback data as training inputs for machine learning algorithms that attempt to identify optimal attribution strategies. The reliability and accuracy of postback data make it particularly valuable for training attribution models that need high-quality conversion data to function effectively.
Cross-channel attribution integration combines postback data with information from other marketing channels to create unified attribution views. This integration helps ensure that server-side tracked conversions are properly attributed within broader marketing attribution frameworks that account for multiple touchpoints and channels.
Real-time attribution updates use postback data to provide immediate attribution feedback that enables responsive campaign optimization. Unlike client-side tracking that may be delayed or incomplete, postback data can provide immediate conversion notifications that support real-time bidding, budget allocation, and campaign management decisions.
Challenges and Limitations
While postback tracking offers significant advantages over client-side methods, it also presents unique challenges and limitations that affiliate marketers must understand and address. These challenges often relate to implementation complexity, data integration requirements, and the need for sophisticated technical infrastructure.
Technical complexity increases significantly with postback implementations compared to simple pixel tracking. Postback systems require server-side development, database integration, security implementation, and ongoing maintenance that may exceed the technical capabilities of smaller affiliate marketers. This complexity can create barriers to adoption and increase implementation costs.
Data synchronization challenges arise when attempting to connect postback conversion data with earlier touchpoint information collected through other tracking methods. Since postbacks typically only provide conversion information, additional systems are needed to maintain customer journey data and enable comprehensive attribution modeling.
Fraud prevention becomes more complex with postback systems because the server-side nature of the communication can make it difficult to verify the authenticity of conversion events. Sophisticated fraud detection systems are needed to prevent fake postback requests and ensure that attribution data reflects genuine conversions.
System reliability requirements increase with postback implementations because server-side failures can result in complete attribution data loss. Unlike client-side tracking where individual user issues don’t affect overall system performance, postback system failures can impact all conversion tracking until resolved.
Integration complexity grows as postback systems must interface with multiple business systems, affiliate networks, and analytics platforms. This integration requires careful coordination and ongoing maintenance to ensure that data flows correctly between different systems and platforms.
Future Developments
The future of postback tracking will likely involve continued evolution to address current limitations while taking advantage of emerging technologies and changing industry requirements. Understanding likely future developments can help affiliate marketers prepare their tracking strategies for continued effectiveness.
Enhanced security measures will likely become standard for postback implementations as fraud prevention becomes increasingly important. These measures might include blockchain-based verification, advanced cryptographic techniques, or AI-powered fraud detection systems that provide stronger protection against fake conversion reports.
Real-time processing capabilities will continue to improve, enabling more immediate attribution feedback and campaign optimization. Future postback systems might provide sub-second conversion notifications that enable real-time bidding optimization and immediate campaign adjustments based on conversion performance.
Machine learning integration will likely become more common as postback systems incorporate AI capabilities for fraud detection, data validation, and attribution modeling. These AI-enhanced systems might automatically detect anomalies, predict attribution patterns, or optimize postback delivery strategies based on historical performance data.
Privacy-preserving techniques may be integrated into postback systems to provide attribution capabilities while protecting individual user privacy. These techniques might use differential privacy, secure multi-party computation, or other cryptographic methods to enable attribution without exposing sensitive customer information.
Standardization efforts may emerge to create industry-wide postback protocols that improve interoperability between different affiliate networks, tracking platforms, and advertiser systems. These standards could reduce implementation complexity while improving data quality and system reliability across the affiliate marketing ecosystem.
Server-Side Tracking: The Future of Attribution {#server-side-tracking}
Server-side tracking represents the most significant evolution in affiliate marketing attribution since the introduction of cookies, offering a comprehensive solution to the privacy and accuracy challenges that have plagued traditional tracking methods. By moving data collection and processing from the client (browser) to the server, this approach provides more reliable attribution while better respecting user privacy preferences. Industry leaders report that server-side tracking can recover 30-40% of conversions that would otherwise be lost to attribution gaps [2].
Architectural Foundations
Server-side tracking fundamentally reimagines how attribution data flows through digital marketing systems. Instead of relying on browser-based technologies that can be blocked or restricted, server-side systems collect and process data on the server, where it can be handled more reliably and securely. This architectural shift addresses many of the core limitations that have reduced the effectiveness of traditional tracking methods.
The data collection layer in server-side tracking systems operates through multiple channels that don’t depend on client-side technologies. These channels might include direct API integrations, webhook notifications, server logs, database triggers, or other server-side data sources that provide comprehensive visibility into user actions and conversions. This multi-channel approach ensures that attribution data is captured even when individual collection methods fail.
Processing engines in server-side tracking systems handle data transformation, validation, and enrichment in real-time or near-real-time. These engines can combine data from multiple sources, apply business logic, perform fraud detection, and execute attribution modeling without relying on client-side processing that may be inconsistent or unavailable. Server-side processing provides more control and reliability compared to browser-based alternatives.
Data storage and management systems in server-side tracking implementations provide secure, scalable repositories for attribution data that can support complex queries and analysis. These systems typically include data warehouses, real-time databases, and analytics platforms that enable comprehensive reporting and optimization. Proper data management is crucial for maintaining attribution accuracy and supporting advanced analytics requirements.
Integration layers connect server-side tracking systems with existing marketing technology stacks, affiliate networks, and business systems. These integrations enable seamless data flow between different platforms while maintaining data consistency and accuracy. Well-designed integration layers reduce implementation complexity while providing flexibility for future system evolution.
Implementation Strategies
Successful server-side tracking implementation requires careful planning and systematic execution that addresses technical requirements, business needs, and privacy compliance obligations. The implementation process typically involves multiple phases that gradually transition from client-side to server-side tracking while maintaining attribution continuity.
Infrastructure planning forms the foundation of effective server-side tracking implementations. This planning must address data volume requirements, processing capabilities, storage needs, security requirements, and integration complexity. Proper infrastructure planning ensures that server-side tracking systems can handle current and future requirements while maintaining performance and reliability.
Data pipeline design defines how information flows through server-side tracking systems from collection to reporting. These pipelines must handle real-time data processing, batch processing, error handling, and data quality validation. Well-designed data pipelines ensure that attribution data is processed accurately and efficiently while providing the flexibility needed for complex attribution modeling.
Security implementation protects server-side tracking systems from unauthorized access, data breaches, and fraud attempts. This implementation includes access controls, data encryption, audit logging, and monitoring systems that ensure data integrity and privacy protection. Strong security is essential for maintaining trust and compliance with privacy regulations.
Testing and validation procedures verify that server-side tracking systems work correctly under various conditions and scenarios. This testing should include data accuracy validation, performance testing, security testing, and integration testing. Comprehensive testing helps identify and resolve issues before they impact live attribution systems.
Migration strategies manage the transition from existing tracking methods to server-side implementations while maintaining attribution continuity. These strategies typically involve parallel tracking periods, gradual feature migration, and careful monitoring to ensure that attribution accuracy is maintained throughout the transition process.
Advanced Capabilities
Server-side tracking enables sophisticated attribution capabilities that are difficult or impossible to achieve with client-side methods. These advanced capabilities provide competitive advantages for affiliate marketers who invest in comprehensive server-side tracking implementations.
Real-time attribution modeling processes conversion data immediately as it occurs, enabling instant campaign optimization and budget allocation decisions. Server-side systems can implement complex attribution models that account for multiple touchpoints, customer characteristics, and business rules without relying on client-side processing that may be delayed or incomplete.
Cross-device attribution becomes more accurate with server-side tracking because it can leverage first-party data, customer databases, and other authoritative data sources to connect user actions across different devices. This capability is particularly valuable for affiliate marketers whose customers frequently switch between devices during their purchase journeys.
Fraud detection and prevention capabilities are enhanced through server-side tracking because all data processing occurs in controlled environments where sophisticated validation and verification can be implemented. These systems can detect suspicious patterns, validate conversion authenticity, and prevent fraudulent attribution claims more effectively than client-side alternatives.
Data enrichment processes combine attribution data with information from CRM systems, customer databases, external data sources, and other business systems to provide comprehensive customer insights. This enrichment enables more sophisticated segmentation, personalization, and optimization strategies that improve campaign performance.
Privacy-compliant attribution techniques use server-side processing to implement privacy-preserving attribution methods that provide marketing insights while protecting individual user privacy. These techniques might include data aggregation, differential privacy, or other methods that balance attribution accuracy with privacy protection.
Integration with First-Party Data
Server-side tracking’s greatest strength lies in its ability to leverage first-party data for attribution purposes, creating more accurate and privacy-compliant tracking systems. This integration enables affiliate marketers to build comprehensive customer profiles that support sophisticated attribution modeling without relying on third-party data sources.
Customer database integration connects server-side tracking with existing customer relationship management systems, enabling attribution based on known customer identities rather than anonymous tracking identifiers. This integration provides more reliable attribution while supporting personalized marketing strategies that improve customer experiences.
Email and marketing automation integration enables server-side tracking to incorporate email engagement data, marketing automation touchpoints, and other owned media interactions into attribution models. This integration provides comprehensive views of customer journeys that include both paid and owned media touchpoints.
E-commerce platform integration connects server-side tracking directly with order management systems, payment processors, and inventory management platforms. This integration ensures that attribution data reflects actual business outcomes and enables sophisticated commission calculations based on real-time business data.
CRM and sales integration enables server-side tracking to incorporate offline sales data, customer service interactions, and other business touchpoints into attribution models. This integration is particularly valuable for high-consideration purchases that involve multiple touchpoints across online and offline channels.
Loyalty program integration connects server-side tracking with customer loyalty systems, enabling attribution models that account for long-term customer value and repeat purchase behavior. This integration supports more sophisticated commission structures that reward affiliates for driving valuable, long-term customers.
Privacy and Compliance Advantages
Server-side tracking provides significant advantages for privacy compliance and data protection compared to traditional client-side methods. These advantages are becoming increasingly important as privacy regulations evolve and consumer expectations change.
Data minimization principles are easier to implement with server-side tracking because data collection and processing can be precisely controlled and limited to necessary information. Unlike client-side tracking that may collect extensive behavioral data, server-side systems can focus on specific attribution data needed for business purposes.
Consent management becomes more straightforward with server-side tracking because it reduces the need for client-side data collection that typically requires explicit user consent. Server-side systems can often operate using legitimate business interests or other legal bases that don’t require explicit consent for every data processing activity.
Data retention and deletion policies are easier to implement and enforce with server-side tracking because all data processing occurs in controlled environments. These systems can automatically implement retention policies, respond to deletion requests, and ensure compliance with privacy regulations more effectively than distributed client-side systems.
Cross-border data transfer compliance is simplified with server-side tracking because data processing can be geographically controlled and limited to appropriate jurisdictions. This control helps ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR that restrict international data transfers.
Audit and transparency capabilities are enhanced through server-side tracking because all data processing activities can be logged and monitored in centralized systems. This capability supports compliance reporting and enables organizations to demonstrate privacy compliance to regulators and customers.
Performance and Scalability
Server-side tracking systems must be designed to handle large volumes of data and complex processing requirements while maintaining high performance and reliability. Understanding performance and scalability considerations is crucial for successful implementation and long-term operation.
Data volume management becomes critical as server-side tracking systems process large amounts of attribution data from multiple sources. These systems must be designed to handle peak loads, seasonal variations, and growth in data volume without performance degradation. Proper capacity planning and scalable architecture are essential for maintaining system performance.
Real-time processing requirements demand sophisticated infrastructure that can handle immediate data processing and attribution calculations. These systems must balance real-time performance with accuracy and reliability, often requiring specialized technologies and architectures that support high-throughput, low-latency processing.
Database optimization ensures that server-side tracking systems can efficiently store and retrieve attribution data for reporting and analysis. This optimization might involve specialized database technologies, indexing strategies, data partitioning, or other techniques that support high-performance data operations.
Caching and performance optimization techniques reduce system load and improve response times for attribution queries and reporting. These techniques might include result caching, query optimization, data pre-aggregation, or other methods that improve system performance without sacrificing accuracy.
Monitoring and alerting systems track server-side tracking performance and notify administrators of issues that might affect attribution accuracy or system availability. These systems should provide detailed performance metrics and proactive alerting that enables quick resolution of performance issues.
Future Evolution
Server-side tracking will continue evolving to address emerging challenges and take advantage of new technologies that enhance attribution accuracy and privacy protection. Understanding likely future developments helps affiliate marketers prepare their tracking strategies for continued effectiveness.
Artificial intelligence integration will likely become standard for server-side tracking systems, enabling more sophisticated attribution modeling, fraud detection, and optimization capabilities. AI-enhanced systems might automatically detect attribution patterns, predict customer behavior, or optimize tracking strategies based on historical performance data.
Privacy-preserving computation techniques such as secure multi-party computation, homomorphic encryption, and differential privacy may be integrated into server-side tracking systems. These techniques could enable attribution modeling and analysis while providing mathematical guarantees of privacy protection.
Blockchain and distributed ledger technologies might be incorporated into server-side tracking systems to provide transparent, tamper-proof attribution records that can be verified by all parties involved in affiliate campaigns. These technologies could address trust and transparency issues while maintaining attribution accuracy.
Edge computing capabilities may be integrated into server-side tracking systems to provide faster processing and reduced latency for real-time attribution applications. Edge computing could enable more responsive attribution systems while reducing bandwidth and infrastructure costs.
Industry standardization efforts may emerge to create common protocols and interfaces for server-side tracking systems. These standards could improve interoperability between different platforms while reducing implementation complexity and costs for affiliate marketers.
GA4 Integration and UTM Best Practices {#ga4-integration}
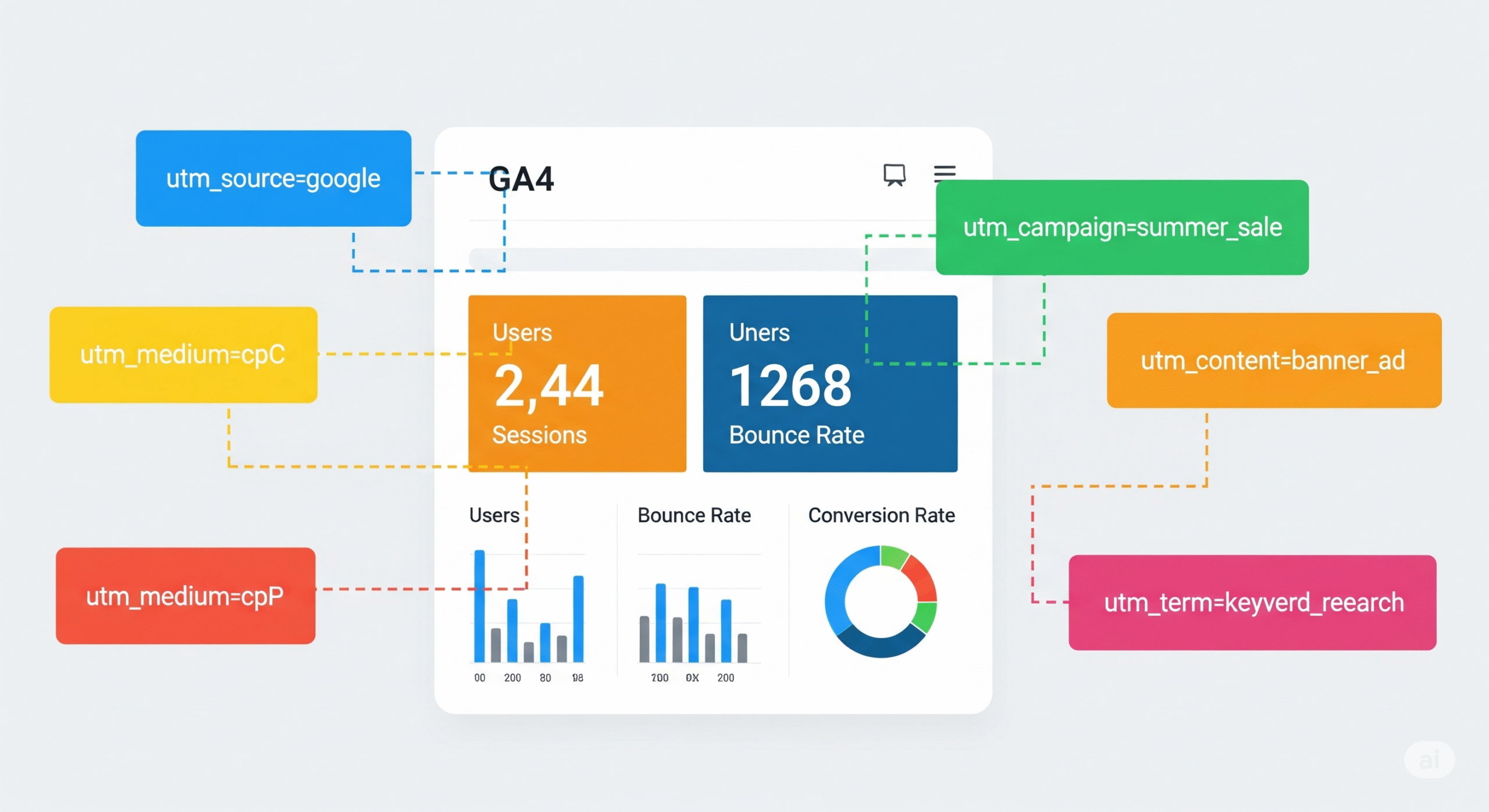
Google Analytics 4 has fundamentally changed how affiliate marketers approach attribution and campaign measurement, introducing new data models, attribution approaches, and integration requirements that affect affiliate tracking strategies. Understanding how to effectively integrate affiliate tracking with GA4 while implementing proper UTM parameter strategies is crucial for comprehensive attribution measurement in 2025.
GA4’s event-based data model requires different approaches to affiliate tracking compared to Universal Analytics. The platform focuses on user engagement events rather than session-based metrics, requiring affiliate marketers to adapt their tracking strategies to align with GA4’s measurement philosophy. Proper event configuration and custom parameter implementation are essential for accurate affiliate attribution within GA4.
UTM parameter strategies for affiliate marketing must balance comprehensive tracking with user experience considerations. Effective UTM implementations enable detailed campaign attribution while maintaining clean, user-friendly URLs that don’t negatively impact conversion rates. Advanced UTM strategies include dynamic parameter generation, automated tagging systems, and integration with affiliate network tracking parameters.
Custom dimensions and metrics in GA4 enable sophisticated affiliate tracking that goes beyond standard e-commerce reporting. These custom implementations can track affiliate-specific data such as commission rates, affiliate partner information, product categories, and other business-specific metrics that support detailed performance analysis and optimization.
Attribution model selection in GA4 significantly impacts how affiliate conversions are credited and reported. Understanding the differences between last-click, first-click, linear, time-decay, and data-driven attribution models helps affiliate marketers choose approaches that align with their business objectives and campaign strategies.
Hybrid Tracking Strategies {#hybrid-strategies}
The most effective affiliate tracking strategies in 2025 combine multiple tracking methods to maximize attribution accuracy while addressing the limitations of individual approaches. Hybrid strategies leverage the strengths of different tracking technologies while providing redundancy that ensures comprehensive attribution coverage.
Multi-method implementation combines pixel tracking, postback systems, and server-side tracking to create comprehensive attribution systems that capture conversions regardless of technical limitations or privacy restrictions. These implementations require careful coordination to prevent double-counting while ensuring maximum attribution coverage.
Fallback mechanisms ensure that attribution data is captured even when primary tracking methods fail. These mechanisms might include alternative tracking pixels, backup postback systems, or manual reporting processes that prevent conversion data loss during system failures or technical issues.
Data reconciliation processes combine data from multiple tracking sources to create unified attribution reports that account for discrepancies between different tracking methods. These processes require sophisticated data processing capabilities and business logic that can resolve conflicts between different data sources.
Privacy Compliance and Data Protection {#privacy-compliance}
Modern affiliate tracking must navigate complex privacy regulations while maintaining attribution accuracy and business effectiveness. Comprehensive privacy compliance strategies address legal requirements while preserving the data insights necessary for campaign optimization and performance measurement.
GDPR compliance for affiliate tracking requires careful attention to legal bases for data processing, consent management, data retention policies, and cross-border data transfer restrictions. Effective compliance strategies balance regulatory requirements with business needs while maintaining user trust and attribution accuracy.
CCPA and state-level privacy law compliance introduces additional requirements for affiliate marketers operating in the United States. These regulations provide users with rights to know what data is collected, request deletion of personal information, and opt out of data sales that can impact affiliate tracking strategies.
Consent management systems enable compliant data collection while maintaining user experience and conversion rates. These systems must balance comprehensive privacy controls with streamlined user experiences that don’t negatively impact affiliate campaign performance.
Implementation Guide and Technical Setup {#implementation-guide}
Successful affiliate tracking implementation requires systematic planning and execution that addresses technical requirements, business objectives, and compliance obligations. This comprehensive implementation guide provides step-by-step guidance for establishing effective tracking systems.
Planning and requirements gathering establish the foundation for successful tracking implementations. This phase should define attribution objectives, technical requirements, compliance obligations, and success metrics that guide implementation decisions and priorities.
Technical architecture design creates the blueprint for tracking system implementation, defining data flows, integration points, security requirements, and scalability considerations. Proper architecture design ensures that tracking systems can meet current and future requirements while maintaining performance and reliability.
Testing and validation procedures verify that tracking implementations work correctly under various conditions and scenarios. Comprehensive testing should include accuracy validation, performance testing, security testing, and compliance verification that ensures tracking systems meet all requirements.
Performance Optimization and Troubleshooting {#optimization-troubleshooting}
Ongoing optimization and maintenance are essential for maintaining tracking accuracy and system performance as affiliate programs grow and evolve. Systematic optimization approaches identify and address performance issues while continuously improving attribution accuracy and system reliability.
Performance monitoring systems track tracking accuracy, system performance, and data quality metrics that enable proactive optimization and issue resolution. These systems should provide detailed analytics and alerting capabilities that support continuous improvement efforts.
Common troubleshooting scenarios include attribution discrepancies, data quality issues, integration problems, and performance degradation. Understanding how to diagnose and resolve these issues quickly is crucial for maintaining tracking effectiveness and campaign performance.
Optimization strategies focus on improving attribution accuracy, reducing system complexity, and enhancing user experience while maintaining comprehensive tracking coverage. These strategies should be based on data analysis and performance metrics rather than assumptions about tracking effectiveness.
Future-Proofing Your Tracking Strategy {#future-proofing}
The affiliate tracking landscape will continue evolving rapidly, driven by privacy regulations, technological advances, and changing user expectations. Future-proofing strategies prepare tracking systems for continued effectiveness despite ongoing changes and uncertainties.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and privacy-preserving computation will likely play increasing roles in affiliate tracking. Understanding these technologies and their potential applications helps affiliate marketers prepare for future tracking evolution.
Regulatory evolution will continue shaping affiliate tracking requirements and capabilities. Staying current with privacy law developments and industry standards helps ensure that tracking strategies remain compliant and effective as regulations evolve.
Industry standardization efforts may create common protocols and best practices that improve interoperability and reduce implementation complexity. Participating in these efforts and adopting emerging standards helps ensure long-term tracking effectiveness.
Conclusion
The affiliate tracking landscape in 2025 requires sophisticated strategies that combine multiple tracking methods, respect user privacy, and provide accurate attribution data for campaign optimization. Success requires understanding the strengths and limitations of different tracking approaches while implementing comprehensive systems that adapt to changing technical and regulatory requirements.
The transition from traditional pixel-based tracking to server-side and hybrid approaches represents a fundamental shift in affiliate marketing attribution. Marketers who invest in understanding and implementing these advanced tracking strategies will maintain competitive advantages while those who rely on outdated methods will face increasing attribution gaps and optimization challenges.
The key to successful affiliate tracking in 2025 lies in balancing attribution accuracy with privacy compliance, technical reliability with implementation complexity, and comprehensive data collection with user experience considerations. This balance requires ongoing attention to industry developments, continuous system optimization, and strategic adaptation to changing requirements.
By implementing the strategies and techniques outlined in this guide, affiliate marketers can build robust tracking systems that provide accurate attribution data while respecting user privacy and complying with regulatory requirements. The investment in proper tracking infrastructure pays dividends through improved campaign optimization, better budget allocation, and more effective affiliate program management.
References
[1] Tracklution – The Complete Guide to Server-Side Tracking in 2025. Available at: https://www.tracklution.com/learn/server-side-tracking-guide-2025/
[2] Scaleo Blog – All Types of Affiliate Tracking Methods (2025 Update). Available at: https://www.scaleo.io/blog/affiliate-network-affiliate-tracking-method-types/
[3] TUNE Blog – Pixels vs Postbacks: Which Tracking Method Should You Use? Available at: https://www.tune.com/blog/hasoffers-pixels-vs-postbacks-tracking-methods/
[4] Analytics Mania – A Guide to UTM Parameters in Google Analytics 4. Available at: https://www.analyticsmania.com/post/utm-parameters-in-google-analytics-4/
[5] Commission Factory – Affiliate Attribution in GA4: What You Need to Know. Available at: https://blog.commissionfactory.com/affiliate-marketing/conversion-tracking-with-ga4-how-to-successfully-navigate-affiliate-channel-attribution
This article was created by Mithun Srivastava- Automate to Profit as part of a comprehensive affiliate marketing content series. For technical implementation support and advanced tracking strategies, consider consulting with attribution specialists or joining affiliate marketing communities focused on tracking and analytics.
